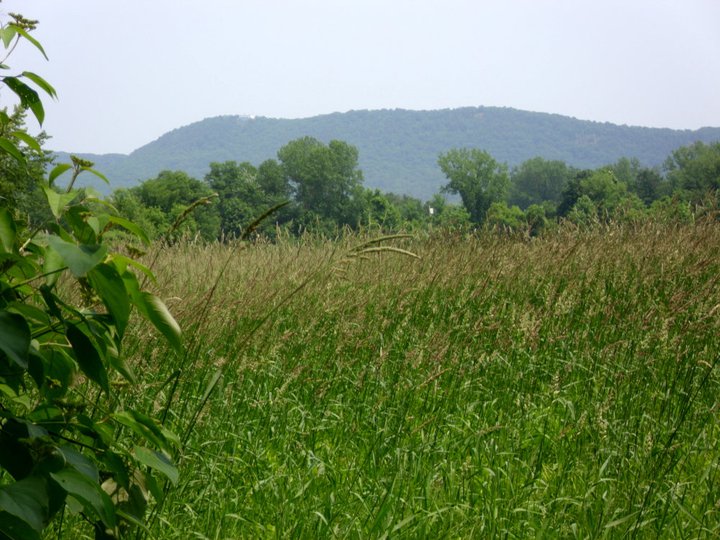

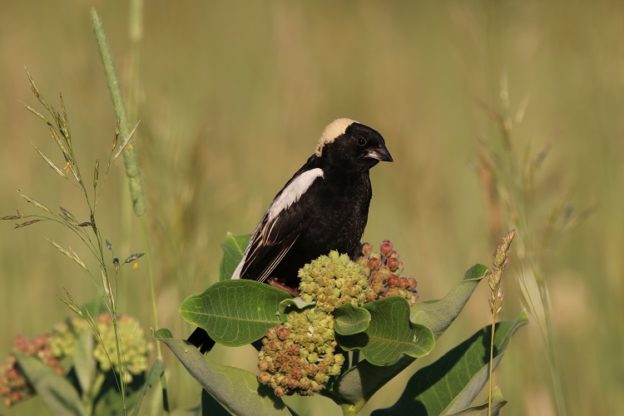
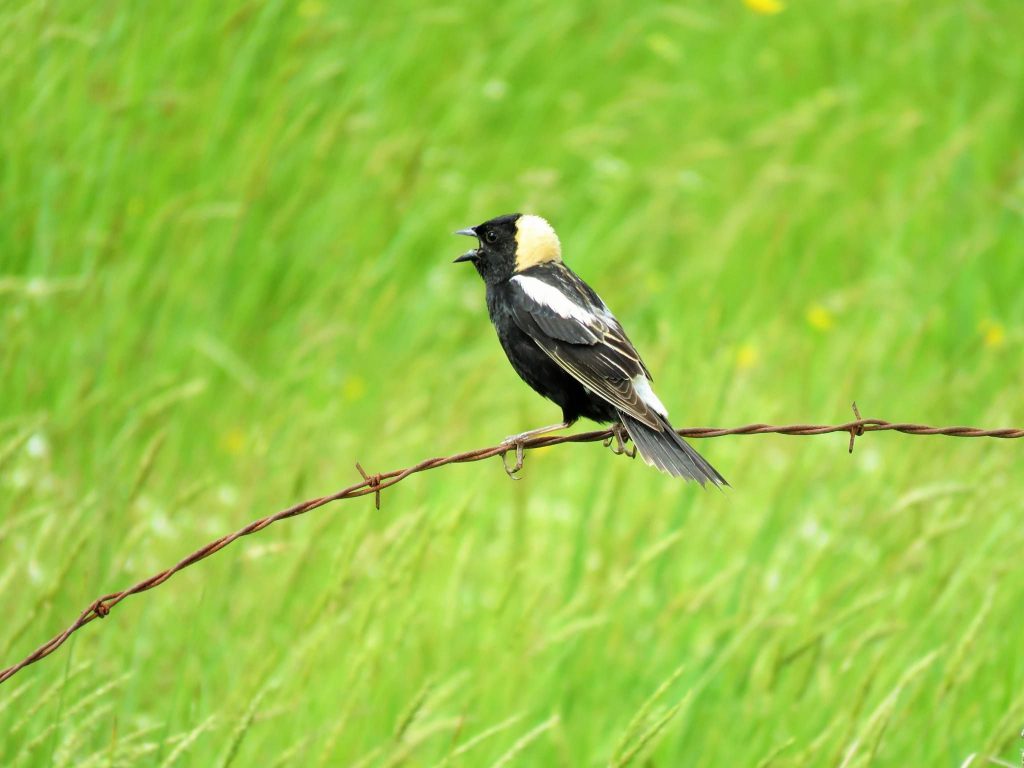
Mass Audubon’s Arcadia Wildlife Sanctuary: a few miles from where Emily Dickinson was inspired by Bobolinks- which have returned to the property thanks to careful stewardship.
References to Bobolinks abound in poetry from 19th-century New England. Massachusetts authors drew inspiration from local birds for a host of reasons, not least because they saw local species as uniquely American subjects (as opposed to, say, the European Nightingale). Bobolinks and Meadowlarks helped distinguish their work from other English-language poets’, and perhaps more importantly, ground it in a sense of place.
Bobolinks were also particularly an familiar and evocative sight through the 1800s and into the past century. Widespread low-impact agriculture provided habitat for field-loving Bobolinks, which don’t mind living near humans as long as their nests are undisturbed. Conspicuous and bold, Bobolinks became an icon of the countryside, and a cultural touchstone for many.
Emily Dickinson, one of rural Massachusetts most-celebrated poets, took a particular liking to them. Bobolinks recurred as a motif in more than 20 of her works. Dickinson often made the birds into rowdy or joyfully anti-authoritarian figures, as here:
Some keep the Sabbath going to Church –
I keep it, staying at Home –
With a Bobolink for a Chorister –
And an Orchard, for a Dome –
Some keep the Sabbath in Surplice –
I, just wear my Wings –
And instead of tolling the Bell, for Church,
Our little Sexton – sings.
God preaches, a noted Clergyman –
And the sermon is never long,
So instead of getting to Heaven, at last –
I’m going, all along.
–Emily Dickinson
Loosely interpreted, the poem emphasizes finding joy in nature and in the everyday. Here, the Bobolink is part of Dickinson’s everyday “Heaven” on earth; its song part of her quiet resistance to organized religion. Dickinson had studied religion in a seminary, but perhaps tellingly, dropped out after a year.
Dickinson always ascribes human qualities to the bird to illustrate a point—whether as a “Sexton” (someone who rings the bells of a church) calling her attention to beauty in nature, or in other poems, as a disruptive “Rowdy of the Meadow.”
Other poets, however, grounded poems in Bobolinks’ natural history and biology, although few connected them with complex societal themes as adroitly as Dickinson. William Cullen Bryant, for example, managed to accurately convey key points about Bobolinks’ seasonal behavior (despite leaning pretty heavily on twee personification and cutesy metaphors):
Merrily swinging on briar and weed,
Near to the nest of his little dame,
Over the mountain-side or mead,
Robert of Lincoln is telling his name:
Bob-o’-link, bob-o’-link,
Spink, spank, spink;
Snug and safe is that nest of ours,
Hidden among the summer flowers;
Chee, chee, chee.
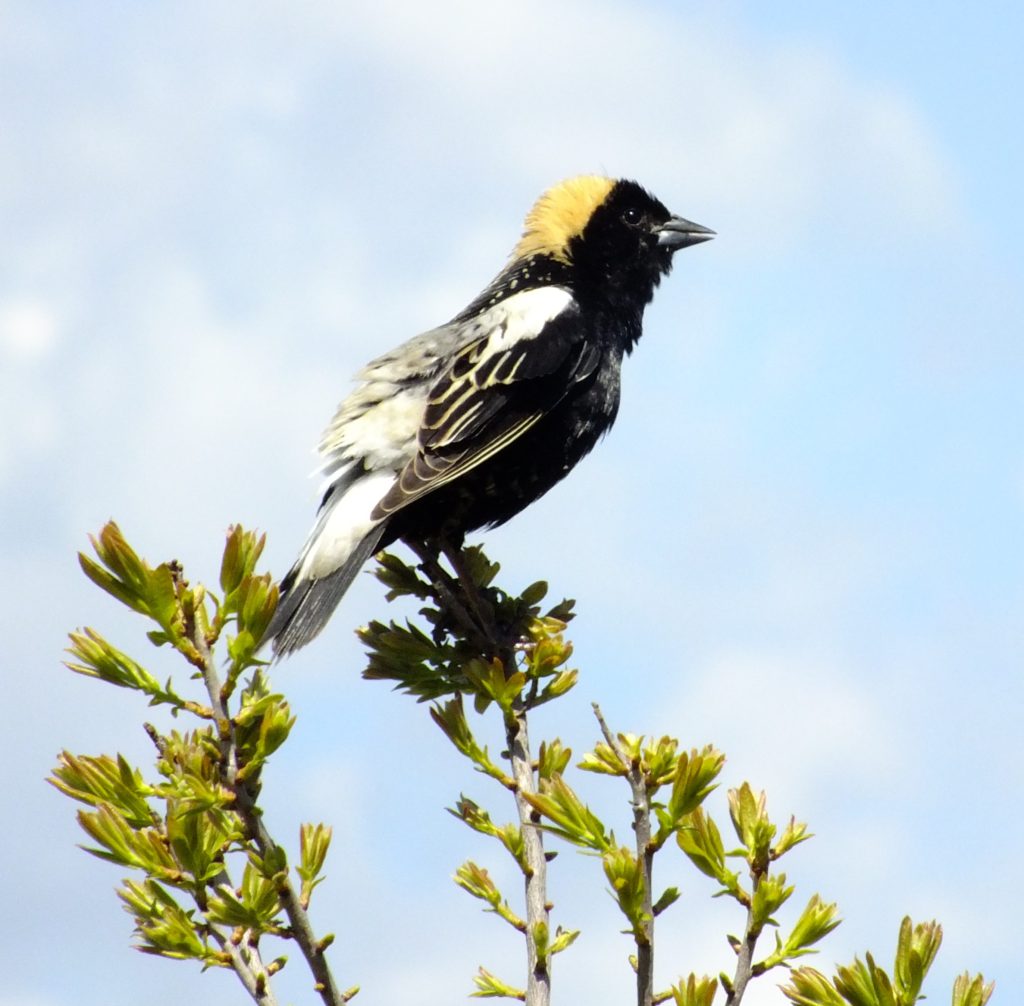
Robert of Lincoln is gaily drest,
Wearing a bright black wedding-coat;
White are his shoulders, and white his crest;
Hear him call in his merry note:
Bob-o’-link, bob-o’-link,
Spink, spank, spink;
Look what a nice new coat is mine,
Sure there was never a bird so fine.
Chee, chee, chee.
Robert of Lincoln’s Quaker wife,
Pretty and quiet, with plain brown wings,
Passing at home a patient life,
Broods in the grass while her husband sings:
Bob-o’-link, bob-o’-link,
Spink, spank, spink;
Brood, kind creature; you need not fear
Thieves and robbers while I am here.
Chee, chee, chee.
Modest and shy as a nun is she;
One weak chirp is her only note,
Braggart and prince of braggarts is he,
Pouring boasts from his little throat:
Bob-o’-link, bob-o’-link,
Spink, spank, spink;
Never was I afraid of man;
Catch me cowardly knaves, if you can !
Chee, chee, chee.
Six white eggs on a bed of hay,
Flecked with purple, a pretty sight!
There as the mother sits all day,
Robert is singing with all his might:
Bob-o’-link, bob-o’-link,
Spink, spank, spink;
Nice good wife, that never goes out,
Keeping house while I frolic about.
Chee, chee, chee.
Soon as the little ones chip the shell,
Six wide mouths are open for food;
Robert of Lincoln bestirs him well,
Gathering seeds for the hungry brood.
Bob-o’-link, bob-o’-link,
Spink, spank, spink;
This new life is likely to be
Hard for a gay young fellow like me.
Chee, chee, chee.
Robert of Lincoln at length is made
Sober with work, and silent with care;
Off is his holiday garment laid,
Half forgotten that merry air:
Bob-o’-link, bob-o’-link,
Spink, spank, spink;
Nobody knows but my mate and I
Where our nest and our nestlings lie.
Chee, chee, chee.
Summer wanes; the children are grown;
Fun and frolic no more he knows;
Robert of Lincoln’s a humdrum crone;
Off he flies, and we sing as he goes :
“Bob-o’-link, bob-o’-link,
Spink, spank, spink;
When you can pipe that merry old strain,
Robert of Lincoln, come back again.
Chee, chee, chee.
– William Cullen Bryant
Bryant’s poem draws a parallel between the Bobolink’s behavioral changes over a breeding season and a human who is burdened with work and worry as they age. But the poem is essentially fanciful, and its goal is mainly to describe these seasonal arcs with flowery language. Still, it’s a rare poem for weaving in a significant amount of natural history.
One could say that Dickinson’s and Bryant’s poems have different goals. Dickinson uses the Bobolink as a device to illustrate the experience of finding joy and religion in nature; she ascribes human qualities to a bird to tell us something about ourselves. Bryant’s poem ascribes human qualities to a bird, but more to illustrate points about the bird itself.
Which poem do you prefer? Do you know of any contemporary poems about Bobolinks—or maybe have written one yourself? Share with us below in the comments!
You can also learn more about (currently-living) Bobolinks and how to protect them at Mass Audubon’s Bobolink Project website.
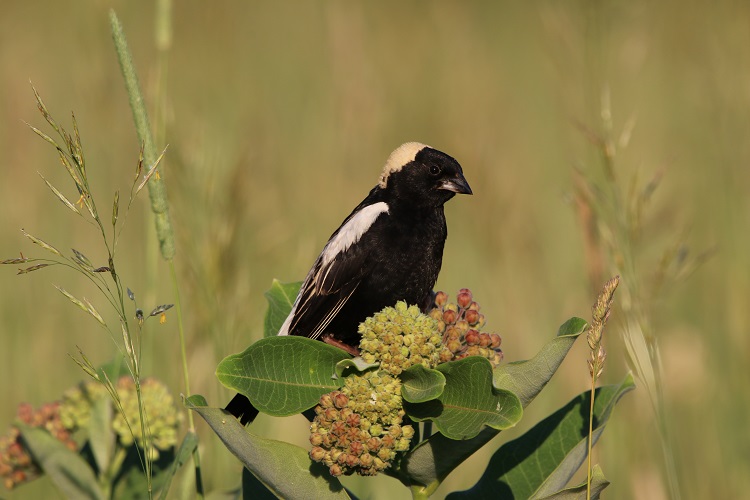
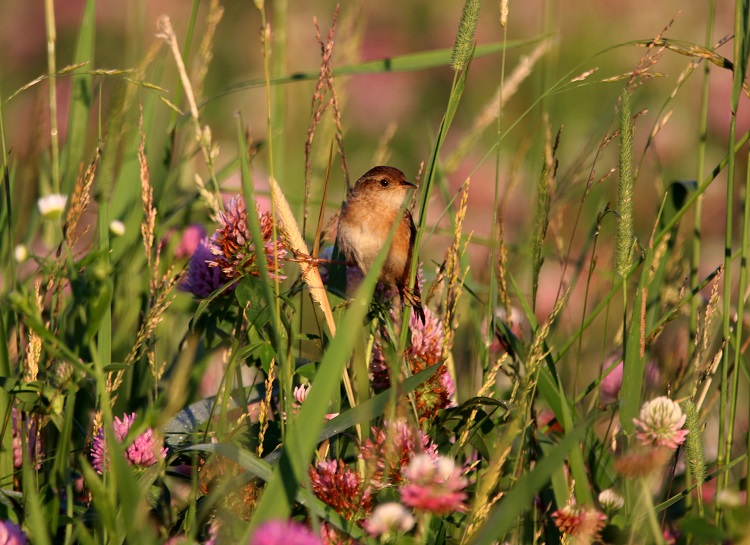












 Calling all birders and bird enthusiasts!
Calling all birders and bird enthusiasts!